Trauma, such as falls or direct impact to the wrist.
.png)
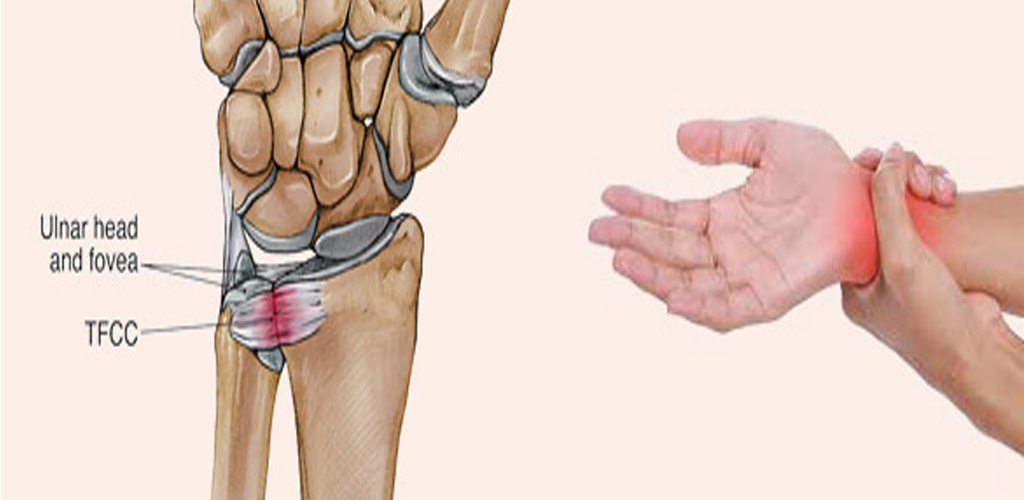
A TFCC Tear, or Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex tear, is an injury affecting the cartilage and ligaments in the wrist. The TFCC, located on the ulnar side of the wrist, plays a crucial role in stabilizing the joint and supporting smooth movement.
TFCC tears can result from various causes, including:
Trauma, such as falls or direct impact to the wrist.
Degeneration over time, especially with repetitive wrist movements.
Distal radius fractures or ulnar impaction syndrome.
Common signs and symptoms of a TFCC tear include:
Persistent pain on the ulnar side of the wrist.
Swelling, particularly on the little finger side of the wrist.
Clicking or popping sounds during wrist movement.
Diagnosing a TFCC tear involves a thorough examination, which may include:
Assessing pain, swelling, and range of motion.
X-rays, MRI, or arthroscopy to visualize the TFCC and surrounding structures.
Treatment for TFCC tears varies based on severity and may include:
Allowing the wrist to rest and heal with splinting or bracing.
Exercises to strengthen the wrist and improve range of motion.
Recovery from a TFCC tear depends on the extent of the injury and chosen treatment. Physical therapy is often crucial for rehabilitation.
If you suspect a TFCC tear or experience persistent wrist pain, consult with a qualified orthopedic specialist for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.