Neurological disorders, such as cerebral palsy, stroke, or traumatic brain injury.
.png)
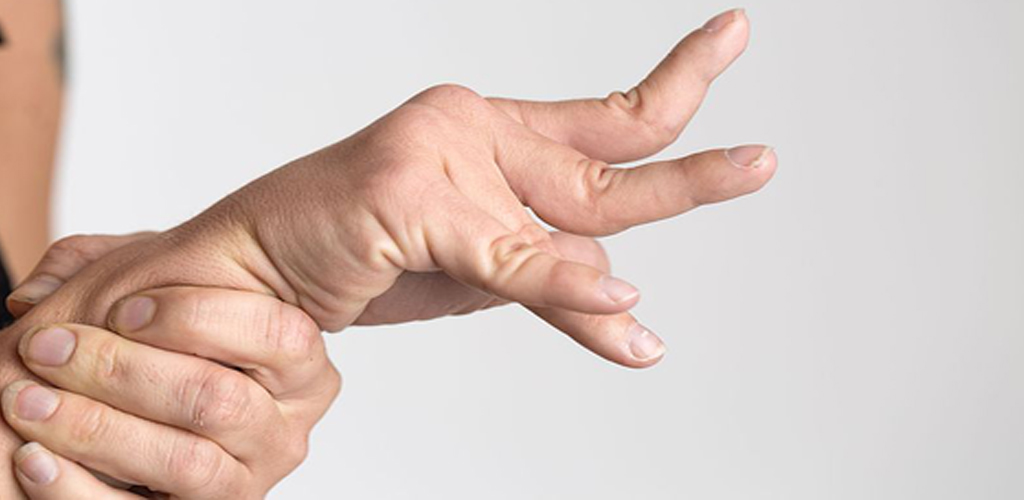
A spastic hand refers to a condition characterized by muscle stiffness and involuntary contractions in the hand. This can be associated with various neurological conditions and may significantly impact hand function. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and management options is essential for individuals experiencing spasticity in their hands.
Neurological disorders, such as cerebral palsy, stroke, or traumatic brain injury.
Spinal cord injuries affecting the nerve signals to the hand muscles.
Multiple sclerosis, a chronic autoimmune disease affecting the central nervous system.
Involuntary muscle contractions leading to stiffness in the hand.
Difficulty in opening or closing the hand voluntarily.
Impaired fine motor skills and hand coordination.
Physical therapy to improve muscle strength, flexibility, and coordination.
Medications, such as muscle relaxants or anti-spasticity drugs, as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Occupational therapy to enhance hand function for daily activities.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of a spastic hand, seeking consultation with a neurologist or rehabilitation specialist is crucial. A comprehensive evaluation can help determine the underlying cause and establish an appropriate management plan for improved hand function and quality of life.