Wrist trauma, such as a fall on an outstretched hand.
.png)
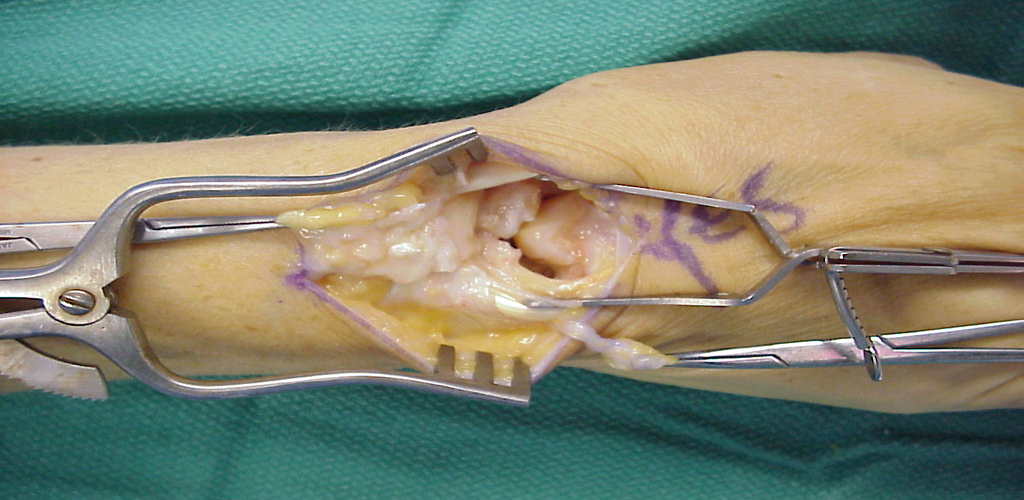
Scapholunate ligament injuries involve damage to the ligament that connects the scaphoid and lunate bones in the wrist. This ligament plays a crucial role in maintaining wrist stability and proper hand function. Injuries to the scapholunate ligament can result in instability and may lead to chronic wrist problems if left untreated.
Scapholunate ligament injuries can occur due to various reasons, including:
Wrist trauma, such as a fall on an outstretched hand.
Repetitive stress on the wrist, common in certain sports or occupations.
Degenerative changes over time.
Common signs and symptoms of scapholunate ligament injuries include:
Wrist pain, particularly on the radial side.
Swelling and tenderness in the wrist.
Decreased grip strength.
Diagnosing scapholunate ligament injuries may involve:
Assessing pain, range of motion, and stability of the wrist.
X-rays, MRI, or arthroscopy for a detailed view of the ligaments and wrist structures.
Treatment for scapholunate ligament injuries depends on the severity and may include:
Wearing a splint or cast to allow the ligament to heal.
Exercises to strengthen the wrist and improve stability.
In severe cases, surgical repair or reconstruction may be recommended.
Recovery from scapholunate ligament injuries requires patience and adherence to the recommended treatment plan. Early intervention often leads to better outcomes.
If you suspect a scapholunate ligament injury or experience persistent wrist pain, consult with a qualified orthopedic specialist for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment.