Nerve Grafting: Involves replacing or repairing damaged nerve segments with grafts from other nerves.
.png)
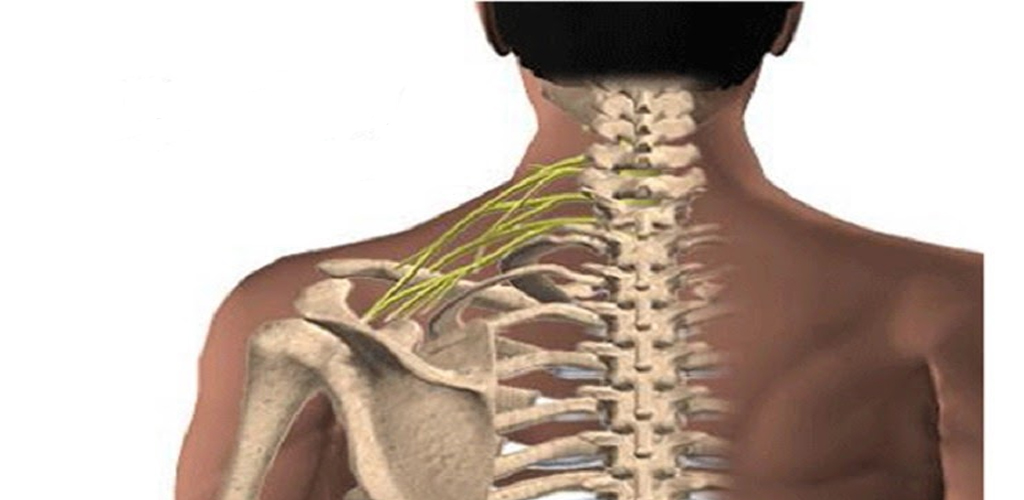
The brachial plexus is a network of nerves that controls the movement and sensation in the shoulders, arms, and hands. Injuries to the brachial plexus can result in significant impairment, requiring surgical interventions to restore function. Understanding the types of brachial plexus surgeries, the procedures involved, and the recovery process is essential for individuals facing these challenges.
Nerve Grafting: Involves replacing or repairing damaged nerve segments with grafts from other nerves.
Nerve Transfer: Redirects a healthy nerve from another muscle or location to the damaged area of the brachial plexus.
Primary Nerve Repair: Directly reconnects the severed or injured nerves without the use of grafts.
Preoperative Evaluation: Detailed assessment of the extent and nature of the brachial plexus injury.
Surgical Intervention: Implementation of the chosen surgical technique, such as nerve grafting or nerve transfer.
Postoperative Care: Monitoring and rehabilitation to support nerve healing and functional recovery.
Accurate testing and diagnosis of a brachial plexus injury involve:
Reviewing the patient's medical history and understanding the circumstances of the injury.
Thorough examination to assess muscle strength, reflexes, and sensory function in the affected area.
Non-surgical approaches for brachial plexus injuries may include:
Targeted exercises to maintain range of motion and prevent muscle atrophy.
Assistance with activities of daily living and strategies to improve functional independence.
Surgical interventions for brachial plexus injuries may involve:
Replacing or repairing damaged nerve segments with grafts from other nerves.
Redirecting a healthy nerve from another muscle or location to the damaged area of the brachial plexus.
The recovery from brachial plexus surgery varies based on the specific procedure and individual factors. It generally involves:
Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises to improve muscle strength, flexibility, and coordination.
Occupational Therapy: Rehabilitation focused on enhancing daily activities and functional independence.
Follow-Up Assessments: Regular evaluations to track progress and make any necessary adjustments to the rehabilitation plan.
If you have experienced a brachial plexus injury or are facing challenges with arm and hand function, consulting with a specialist in brachial plexus surgery is crucial. A comprehensive evaluation will help determine the most appropriate surgical approach and rehabilitation plan for your unique needs.