Postaxial Polydactyly: Extra digits appear on the ulnar side (pinky side) of the hand or foot.
.png)
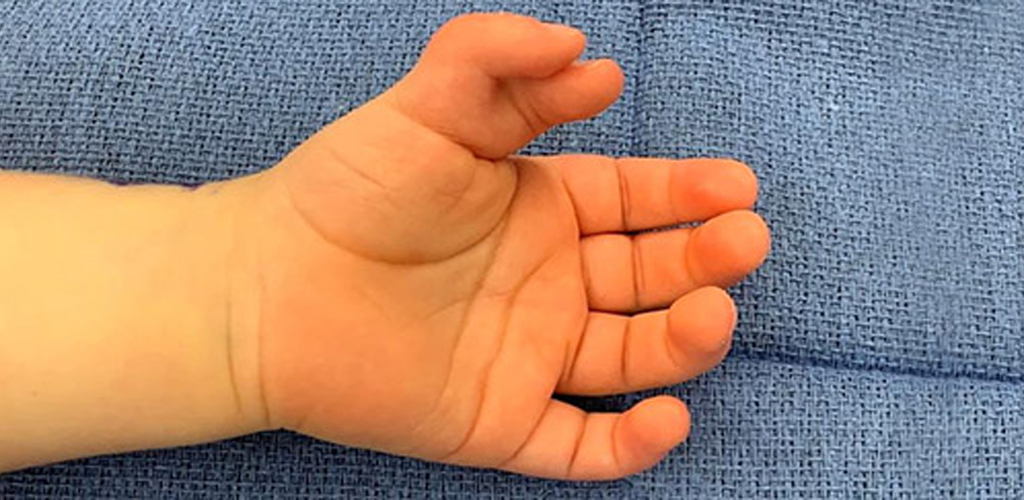
Polydactyly is a congenital condition characterized by the presence of extra fingers or toes on the hands or feet. This condition results from abnormal development during fetal growth and can vary in severity, with the additional digits ranging from small, non-functional structures to fully formed and functional fingers or toes.
Polydactyly can be classified into different types based on the location and characteristics of the extra digits. Common types include:
Postaxial Polydactyly: Extra digits appear on the ulnar side (pinky side) of the hand or foot.
Preaxial Polydactyly: Extra digits appear on the radial side (thumb side) of the hand or foot.
Central Polydactyly: Extra digits appear in the middle of the hand or foot.
Individuals with Polydactyly may exhibit the following symptoms:
Presence of extra fingers or toes.
Varying sizes and shapes of the extra digits.
Potential functional limitations depending on the size and structure of the extra digits.
The exact cause of Polydactyly is often unknown, but it may be influenced by genetic factors and environmental factors during fetal development.
Diagnosing Polydactyly involves a comprehensive evaluation, including:
A thorough examination of the hands or feet to assess the presence and characteristics of extra digits.
X-rays or other imaging techniques to visualize the bones and structures in the affected area.
Genetic testing may be recommended to identify potential underlying genetic causes.
The management of Polydactyly may involve:
Removal or reconstruction of the extra digits to improve hand or foot function and appearance.
Rehabilitative therapies to optimize function and mobility after surgery.
If you or your child is affected by Polydactyly, our specialized team is ready to provide personalized care. Schedule a consultation to discuss tailored solutions that address the unique needs of Polydactyly and enhance overall hand or foot function.